 A cell is a mass of cytoplasm that is bound externally by a cell membrane. Usually microscopic in size, cells are the smallest structural units of living matter and compose all living things. Most cells have one or more nuclei and other organelles that carry out a variety of tasks.
A cell is a mass of cytoplasm that is bound externally by a cell membrane. Usually microscopic in size, cells are the smallest structural units of living matter and compose all living things. Most cells have one or more nuclei and other organelles that carry out a variety of tasks. Publisher of over 50 scientific journals across the life, physical, earth, and health sciences, both independently and in partnership with scientific societies including Cell, Neuron, Immunity, Current Biology, AJHG, and the Trends Journals.
Publisher of over 50 scientific journals across the life, physical, earth, and health sciences, both independently and in partnership with scientific societies including Cell, Neuron, Immunity, Current Biology, AJHG, and the Trends Journals.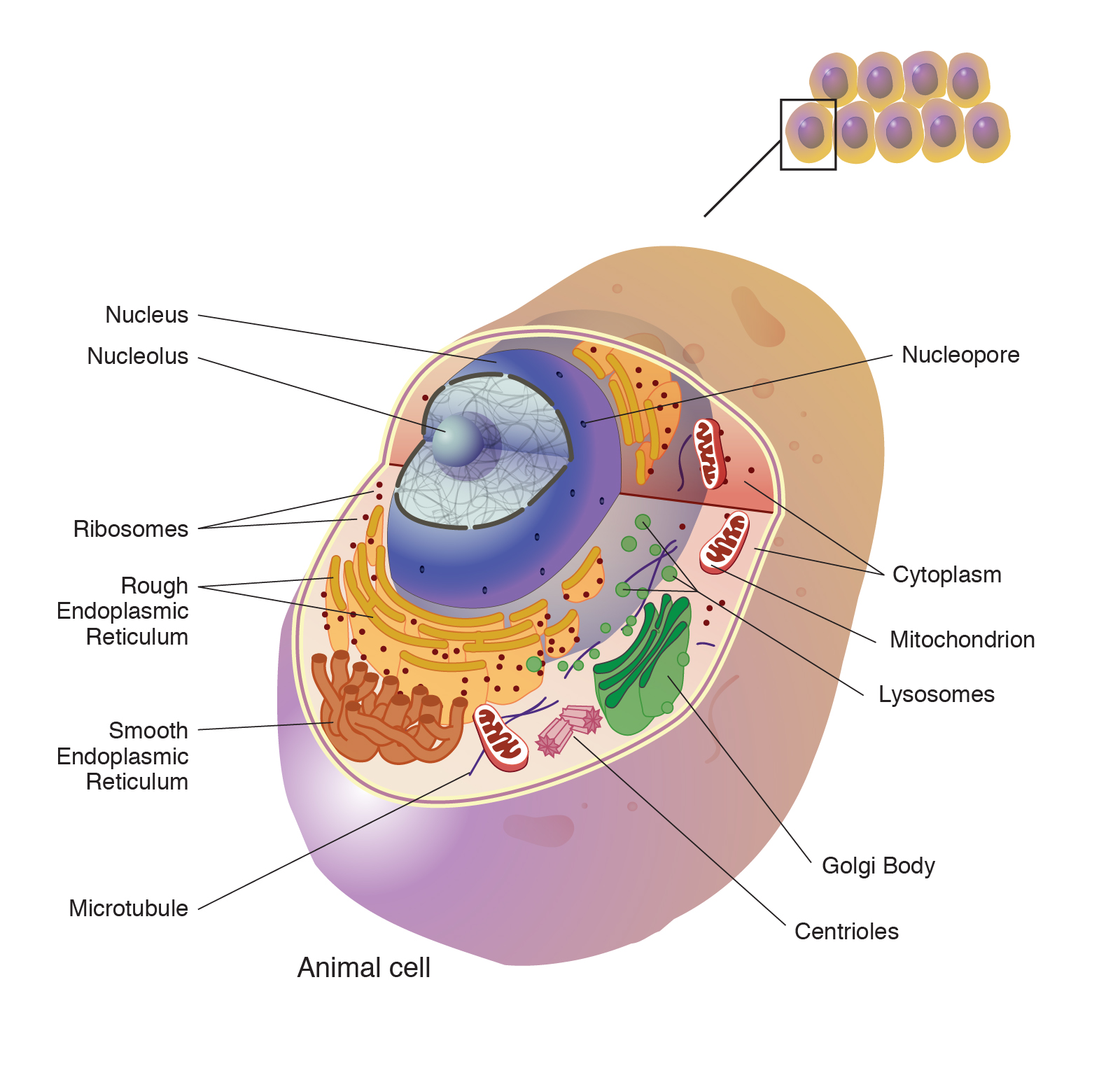 All cells can be sorted into one of two groups: eukaryotes and prokaryotes. A eukaryote has a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while a prokaryote does not. Plants and animals are made of numerous eukaryotic cells, while many microbes, such as bacteria, consist of single cells.
All cells can be sorted into one of two groups: eukaryotes and prokaryotes. A eukaryote has a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while a prokaryote does not. Plants and animals are made of numerous eukaryotic cells, while many microbes, such as bacteria, consist of single cells.